In today’s energy landscape, where industries are under growing pressure to optimize operational costs, reduce carbon footprints, and ensure uninterrupted power, one technology stands out for its versatility and game-changing potential: the solar hybrid inverter. For large manufacturing units, warehouses, commercial buildings, agro-industrial setups, and C&I facilities, the need for energy reliability is non-negotiable. Production lines must run continuously. Machinery requires consistent voltage. Operations cannot afford even a minute of downtime. At the same time, rising electricity tariffs, diesel generator expenses, and grid instability increase financial and operational burdens.
This is exactly where solar hybrid inverters come in – combining the intelligence of smart power management with the reliability of hybrid energy sources. They help industries shift from reactive energy management to proactive, sustainable, and cost-efficient control.
Table of Contents
In this comprehensive, in-depth guide, we explore everything you need to know about solar hybrid inverters, how they work, their key advantages, installation considerations, technology trends, and why they are becoming the backbone of solar power for industries worldwide. Whether you are an industrial decision-maker evaluating solar investments or a business leader planning long-term energy resilience, this guide empowers you with clear, actionable insights.
What Is a Solar Hybrid Inverter?
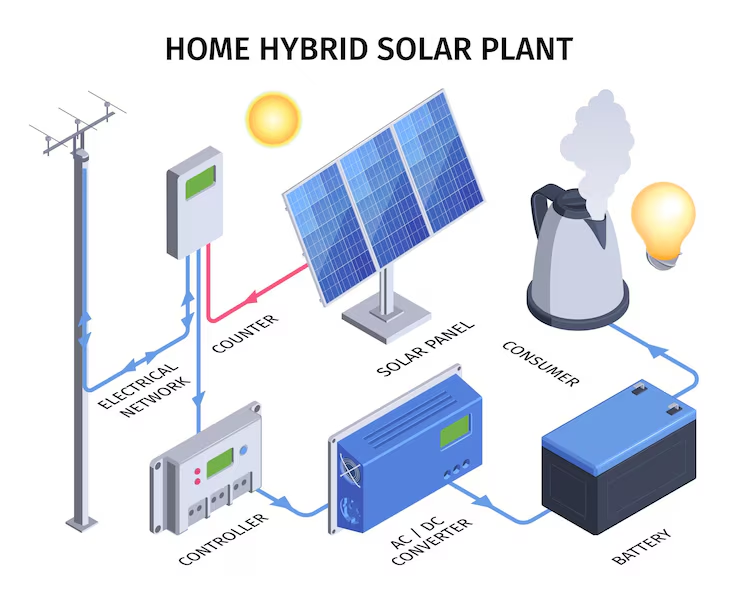
A solar hybrid inverter, also known as a multi-mode or intelligent inverter, is a versatile power-conversion device that integrates various functions: it converts DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity (solar PV inverter), manages the charging and discharging of battery systems (battery inverter/charger), and optionally interacts with the utility grid by importing from or exporting to it. This advanced device serves as a central management unit in modern solar power setups, intelligently directing energy flows among solar panels, battery storage, and the grid, ensuring efficient energy usage whenever and wherever needed.
How Does a Solar Hybrid Inverter Work?
Here’s a breakdown of the working principle:
1. DC-AC Conversion
Solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity, which is not suitable for machines and industrial equipment. To make this energy usable, a hybrid inverter is employed to convert the generated DC into alternating current (AC) power, aligning it with the electrical requirements of the facility. The conversion process utilizes power electronics components, such as Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs), and is controlled by pulse-width modulation (PWM) technology. This ensures a stable, grid-compatible AC output. The primary function of the hybrid inverter is the transformation from DC to AC power, achieved by activating and deactivating the power electronic switch in synchronization with PWM technology, which helps maintain the desired voltage and frequency stability.
2. Battery Management
The hybrid inverter features an integrated energy storage management system that allows for real-time monitoring of the energy storage battery’s status, including power, voltage, and temperature. This system intelligently controls the charging and discharging of the battery based on grid conditions and power demands. When the grid supply is ample and sunlight is strong, excess solar power is stored in the battery. Conversely, during grid outages or insufficient sunlight, the inverter automatically shifts to battery power supply mode, ensuring an uninterrupted power supply to the load.
Furthermore, when there is surplus solar power beyond the load requirements, the inverter utilizes this excess to charge the battery while constantly monitoring battery parameters to ensure safe operation. In cases of low solar generation or power outages, the inverter draws from the battery, converting the stored DC power back into AC to supply energy to the facility.
3. Intelligent Scheduling
The hybrid inverter features an intelligent scheduling function powered by a built-in microprocessor and control circuit. This allows the inverter to monitor real-time grid parameters such as voltage, current, and frequency, enabling automatic adjustments based on a preset scheduling strategy. For instance, during periods of high power consumption, it can discharge battery power to the grid, alleviating grid pressure. Conversely, during low consumption, excess power is stored in the battery for potential emergencies. The inverter can also be programmed for various operational modes including “self-consumption,” “backup,” and “time-of-use optimization.”
4. Grid Interaction
A hybrid solar inverter facilitates interaction with the electrical grid by allowing users to import grid power when solar energy and battery storage are insufficient to meet energy demand. It enables the export of surplus electricity back to the grid when there is excess solar generation or battery storage, which can lead to credits or lowered energy bills through net metering programs. The inverter synchronizes its AC output with the grid during these transactions. Additionally, in the event of a grid loss, it can function independently by isolating itself from the grid and drawing power from its battery system.
Types of Solar Hybrid Inverters
1. AC-Coupled Hybrid Inverters
This design facilitates the integration of battery systems on the AC side of existing solar plants, making it suitable for retrofitting battery storage in grid-connected setups. It offers easy compatibility with older inverters, flexibility in installation, and is particularly advantageous for factories looking to upgrade their current solar configurations. While installation is simplified, it’s important to note that there may be a minor efficiency loss due to the necessity of multiple conversion stages during the process.
2. DC-Coupled Hybrid Inverters
Both solar panels and batteries are interconnected on the DC side, which enhances system efficiency by reducing energy conversion losses. The inverter in this setup features a DC-DC stage for effective battery charge and discharge management, alongside an MPPT (maximum power point tracker) specifically for solar panels. This configuration is particularly advantageous for large solar and battery systems, as it offers higher efficiency and is well-suited for industries operating for extended hours.
3. Grid-Tied Hybrid Inverters
These inverters are designed to operate with both solar energy systems and energy storage solutions while maintaining a connection to the main electrical grid. They facilitate the export of excess electricity generated by solar panels, thereby potentially reducing daytime energy costs for users. This functionality makes them particularly suitable for urban industries that rely on consistent grid power. The inverters enable users to feed surplus solar energy back to the grid, contingent on the availability of net metering or export agreements. Additionally, they manage the processes of battery charging and discharging. Overall, these inverters are advantageous for industrial applications seeking to enhance self-consumption of energy while capitalizing on any surplus generated electricity.
4. Off-Grid Hybrid Inverters
Built for complete independence from the electric grid, these systems integrate solar power, batteries, and sometimes diesel generators, making them ideal for remote industrial sites. They are designed to function effectively in areas with weak or non-existent grid connections, providing long backup power. These systems efficiently manage the coordination of solar charging, battery discharge, and generator input, proving beneficial for remote industrial facilities and microgrids.
5. Multi-Mode (or All-In-One) Hybrid Inverters
These versatile systems integrate multiple functions, including Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT), inverter capabilities, and battery charging, all within a compact unit. They facilitate simplified installation and smart energy management, making them particularly suitable for commercial and industrial (C&I) rooftops where space is limited. Their flexibility allows operation in grid-tied, off-grid, and battery backup modes, ensuring a smooth transition between different power sources. These systems are commonly employed in applications that necessitate both energy export and backup features.
6. Low-Voltage vs High-Voltage Hybrid Inverters
Low-Voltage Inverters are compatible with low-voltage battery banks, such as 48 V, and are popular for small to mid-scale systems requiring moderate backup. They are cost-effective, easy to maintain, and suitable for use in office blocks, workshops, and small units. In contrast, High-Voltage Inverters are designed specifically for high-voltage battery systems exceeding 150 V. These inverters offer higher efficiency and support faster charging, making them ideal for heavy industrial loads and large battery banks. They enhance system performance and are best suited for high-demand factories and operations running 24/7, facilitating faster battery recharge.

Key Components of a Solar Hybrid Inverter
1. MPPT Charge Controller
The Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is a critical component of solar inverters, functioning as a “power optimizer.” It continuously adjusts the solar input voltage to ensure the extraction of the maximum possible energy from photovoltaic (PV) panels, even under variable conditions such as cloud cover or temperature changes. Key benefits of MPPT include enhanced efficiency, stable power extraction, and its fundamental role in large commercial and industrial (C&I) solar systems. MPPT technology enables precise tracking of the maximum power point of solar panels, facilitating optimal energy retrieval. Additionally, it effectively regulates voltage and current into the DC bus, thereby supporting rapid and efficient charging, regardless of fluctuations in sunlight or environmental conditions.
2. DC–DC Converter
This document describes a module that converts and stabilizes various DC voltages from sources like photovoltaic (PV) panels and batteries to ensure a common DC bus. It collaborates with the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) system to optimize power flow into the batteries. The module is responsible for regulating and conditioning the DC power, which facilitates smooth charging and discharging of the battery bank while maintaining voltage stability throughout the system. Key features include battery protection, improved conversion efficiency, and support for both low voltage (LV) and high voltage (HV) battery systems.
3. Inverter (DC → AC Conversion Stage)
This document describes the core function of a hybrid inverter, which is to convert direct current (DC) from solar panels and batteries into alternating current (AC) compatible with electrical appliances and the grid. Key features include stable frequency and voltage output, compatibility with both grid and load, and the provision of clean power essential for delicate machinery. The inverter employs semiconductor switches such as IGBTs or MOSFETs to create a stable, clean AC waveform while utilizing high-frequency switching to optimize efficiency.
4. Battery Management System (BMS)
The Battery Management System (BMS) is designed to monitor and protect battery banks from several critical issues, including overcharging, over-discharging, overheating, and imbalanced cells. Its primary function is to ensure the batteries maintain longevity and peak performance, which is especially vital for industrial energy storage applications. The BMS prioritizes safety and incorporates smart tracking for battery health, supporting various battery chemistries such as lithium and gel. It continuously monitors the state-of-charge (SoC), temperature, and voltage of individual battery cells. Additionally, it manages charging and discharging processes safely, preventing overcharging or deep discharge, and communicates with the inverter to optimize charging profiles according to the specific battery chemistry used.
5. Cooling System
Hybrid inverters generate heat during power conversion, making efficient cooling essential for optimal performance. This can be achieved through smart fans (active) or passive heat sinks, which contribute to enhanced durability, ensure stable operation even in harsh weather conditions, and reduce the risk of thermal shutdown. Proper thermal management protects internal components, increasing both reliability and lifespan of the system.
6. Communication & Monitoring Module
Modern hybrid inverters are equipped with Wi-Fi or RS-485 connectivity for live data and remote monitoring through apps or web dashboards. They allow tracking of various parameters including solar generation, battery health, load consumption, grid import/export, and system efficiency. This capability supports data-driven energy decisions, making them ideal for multi-unit industrial campuses and aiding in achieving sustainability KPIs. Additionally, interfaces such as Wi-Fi, RS-485, CAN, and Modbus enable real-time monitoring, while a data logger and user interface, whether LCD or LED, help users track system health and performance effectively.
7. AC / DC Input-Output Terminals
These terminals serve as connection points for the inverter, facilitating connections between the solar array, battery bank, grid supply, and industrial loads. They support clean wiring and ensure stable power flow, making them ideal for high-current industrial environments. Specifically designed for the safety and efficiency required in such settings, the terminals accommodate inputs from solar panels (DC), battery banks (DC), as well as grid power (AC) and industrial loads (AC).
Benefits of Solar Hybrid Inverters for Industrial & Commercial Units
1. Lower Electricity Bills
A Solar Hybrid Inverter maximizes the use of onsite solar energy by storing excess generation for later use, allowing industries to significantly cut electricity expenses. With its ability to supply battery power during peak tariff hours, a Solar Hybrid Inverter helps reduce grid dependence and minimize the use of costly diesel generators. This leads to substantial savings in monthly operational costs—an essential advantage for energy-intensive manufacturing units.
2. Smart Energy Management & Load Optimization
A modern Solar Hybrid Inverter is equipped with advanced energy management systems capable of intelligently switching between solar power, battery storage, and grid supply based on real-time demand. This ensures precise peak-load management, eliminates penalties from sudden load spikes, and optimizes power usage across various shifts. The strategic use of a Solar Hybrid Inverter allows industries to maintain smooth operations even during fluctuating energy demands.
3. Scalability & Flexibility
One of the biggest advantages of a Solar Hybrid Inverter is its scalability. Commercial and industrial facilities can easily expand their energy systems by adding more solar panels or increasing battery capacity as their power requirements grow. A Solar Hybrid Inverter integrates seamlessly with existing electrical infrastructure, allowing businesses to start small and scale over time. This flexibility makes a Solar Hybrid Inverter a future-ready investment for companies planning long-term expansion.
4. Improved Power Quality
A Solar Hybrid Inverter plays a critical role in improving overall power quality for industrial units. By storing energy during low-demand periods and deploying it during high-demand peaks, it ensures stable and reliable power delivery. The inverter also minimizes voltage fluctuations, reduces harmonic distortion, and delivers clean, consistent AC output. This ensures smoother operation of sensitive machinery and prolongs equipment lifespan—making the Solar Hybrid Inverter indispensable for high-load environments.
5. Reduced Carbon Footprint
Using a Solar Hybrid Inverter enables businesses to optimize solar consumption and reduce reliance on fossil-fuel-based backup systems. By cutting down diesel usage and lowering greenhouse gas emissions, companies can strengthen their sustainability efforts and improve ESG reporting. A Solar Hybrid Inverter helps industries meet global environmental standards while enhancing their reputation as responsible and eco-conscious brands.
6. Better Power Quality & Reliability
For industries that require uninterrupted operations, a Solar Hybrid Inverter ensures superior power reliability. It mitigates voltage sags, regulates power fluctuations, and delivers a consistent energy supply, even during grid disturbances. This results in fewer outages, better machine performance, and enhanced operational continuity—key factors for manufacturing facilities running critical processes.
7. Advanced Monitoring & Remote Control
Today’s Solar Hybrid Inverter systems come with smart monitoring tools, offering complete visibility into energy production, load consumption, and battery performance. Through user-friendly dashboards, remote diagnostics, and real-time analytics, facility managers can track and optimize power usage with precision. These intelligent controls make the Solar Hybrid Inverter a powerful tool for data-driven decision-making and long-term operational efficiency.
Solar Hybrid Inverter vs Traditional Solar Inverter
| Parameter | Solar Hybrid Inverter | Traditional Solar Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Works with solar, grid, and battery simultaneously | Works only with solar and grid |
| Backup Capability | Provides power backup through batteries | No backup—shuts down during grid failure |
| Energy Management | Smart management: prioritizes solar, then battery, then grid | Limited control; grid-dependent |
| Ideal For | Industries requiring continuous power and peak-load management | Areas with stable grid and no backup requirement |
| Energy Storage Support | Enabled (Lithium-ion, Lead-acid, etc.) | Not supported |
| Efficiency | Higher due to optimized DC & AC power flow | Moderate; loses power during conversion |
| Grid Outage Handling | Seamless transition; uninterrupted operations | Stops functioning when grid is down |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for C&I applications | Moderate scalability |
| Operational Cost Savings | Higher savings via load shifting + solar + storage | Limited savings; grid reliance remains high |
| Capex | Slightly higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Faster ROI due to energy savings & backup value | ROI depends only on solar generation |
| Advanced Features | Smart monitoring, peak shaving, demand response | Basic monitoring; no peak management |
| Best Use Cases | Manufacturing, heavy machinery, 24/7 units, critical loads | Office buildings, small facilities, low-load operations |
Applications of Solar Hybrid Inverters in Industries
A Solar Hybrid Inverter has become a cornerstone of modern industrial energy systems, offering unmatched reliability, efficiency, and adaptability. By intelligently combining solar power, battery storage, and grid supply, it empowers industries to maintain operational continuity, reduce energy costs, and scale sustainably in a rapidly evolving energy landscape. Below is a comprehensive look at how different sectors are deploying this advanced technology to transform their power infrastructure.
1. Manufacturing & Heavy Industries
Manufacturing units heavily rely on high-demand equipment such as motors, crushers, compressors, and CNC machines, where even brief power dips can lead to significant production losses. A Solar Hybrid Inverter offers several advantages, including ensuring a continuous power supply during outages, facilitating smoother machine operation with stable voltage, and lowering daytime electricity costs through optimized solar usage. Additionally, it reduces fuel consumption by minimizing the runtime of diesel generators. This technology is particularly beneficial in industries such as automotive, engineering, textile, chemical, and steel, which require 24/7 operational reliability.
2. Industrial Warehouses, Storage & Logistics Hubs
Large warehouses rely on consistent lighting, automated systems, conveyor belts, and HVAC operations. A Solar Hybrid Inverter benefits these facilities by providing backup power during loading and unloading, supplying energy during evening and night-time operations through stored solar energy, and mitigating energy spikes associated with heavy equipment usage. This system facilitates a seamless logistics flow, reducing reliance on unstable grid power.
3. Cold Storage & Food Processing Industries
Temperature-controlled operations require stable energy supply, and utilizing a Solar Hybrid Inverter addresses this need. Such inverters provide continuous refrigeration, lower grid consumption, and reduced diesel usage. The stability they offer ensures product quality is maintained, resulting in enhanced storage reliability and decreased operational costs.
4. Metal Fabrication, Welding & High-Load Workshops
These units frequently experience voltage fluctuations caused by the high demand from heavy equipment. A Solar Hybrid Inverter addresses these issues by providing clean and stable AC output, reducing harmonic distortion, correcting power factor, and offering high-load support during peak work hours. These features enhance performance, protect tools, and prevent production delays.
5. Data Centers & IT Infrastructure
Data centers depend on a reliable and stable energy supply to operate effectively. The implementation of a Solar Hybrid Inverter facilitates several key improvements, including instantaneous backup capabilities without delays during switching, efficient load balancing among various power sources, and a marked decrease in reliance on uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and diesel generators. Consequently, this technology leads to enhanced system uptime and a reduced operational carbon footprint.
6. Pharmaceutical Units & Clean Room Operations
Precision-driven environments necessitate enhanced power quality, which is achieved through a Solar Hybrid Inverter. This technology provides regulated voltage essential for sensitive instruments, ensures a reliable power supply to HVAC and air filtration systems, and maintains compliance with rigorous quality and safety standards. Consequently, hybrid systems become crucial in pharmaceutical, research and development laboratories, as well as biotech facilities.
7. Remote Sites, Mining Operations & Off-Grid Plants
In areas with limited power grid reliability or in remote locations, power interruptions frequently occur. The Solar Hybrid Inverter addresses this issue by offering efficient off-grid operation, seamless integration of diesel generators, solar energy, and battery systems, as well as long-duration backup for isolated units. These features significantly improve productivity in sectors such as mining, oil and gas, and rural industrial environments.
8. Commercial Buildings, Retail Chains & Corporate Offices
Hybrid inverters are highly effective in commercial settings, particularly in managing high daytime loads such as HVAC systems, lifts, lighting, and servers. They are capable of peak shaving to mitigate demand penalties and providing backup power for essential office infrastructure. By utilizing a Solar Hybrid Inverter, businesses can establish a reliable and sustainable energy ecosystem that enhances overall business continuity.

EV Charging Stations & Smart Infrastructure
1. Clean, Renewable Charging Power
EV charging stations experience significant energy demand, particularly during peak hours. A Solar Hybrid Inverter addresses this challenge by leveraging solar power during daylight hours to charge electric vehicles (EVs). It allows for the storage of excess solar energy in batteries, which can be utilized for charging in the evening and at night. This system reduces the amount of energy purchased from the grid, resulting in lower operational costs per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Consequently, industries and commercial units can provide eco-friendly EV charging services at competitive prices. The solar hybrid inverter prioritizes solar energy, utilizes stored battery power when necessary, and resorts to grid power only as a last option, ensuring that EVs are predominantly charged with renewable energy.
2. Grid Load Management
With the intelligence of a hybrid inverter, charging stations can implement peak-shaving techniques, utilizing stored battery energy during periods of high demand rather than relying on the grid. The high power consumption from electric vehicle (EV) chargers can create strain on the electrical grid. However, by employing a Solar Hybrid Inverter, facilities can effectively shift their energy loads to stored solar power, sidestepping peak-time tariff charges, alleviating grid overload when demand is high, and maintaining voltage stability throughout the infrastructure. This approach enhances the reliability of EV charging stations and promotes a more grid-friendly operation.
3. Backup for Uninterrupted Charging
Grid failures can hinder electric vehicle (EV) charging operations and negatively affect customer experience. The Solar Hybrid Inverter, equipped with integrated battery storage, provides a solution by ensuring seamless charging even during grid outages, resulting in zero downtime for charging stations. This system maintains continuous operation of essential services such as payment kiosks, lighting, and communication systems. It is particularly suited for corporate fleets, logistics hubs, and public charging stations. In the event of a grid outage, the hybrid inverter can swiftly transition to using battery and solar power, thereby keeping EV chargers and critical infrastructure operational.
4. Smart Monitoring & Control
Modern electric vehicle (EV) charging stations necessitate real-time monitoring for various functions including performance evaluation, billing processes, and energy management. A Solar Hybrid Inverter enhances these capabilities through several smart features such as mobile app connectivity, cloud-driven dashboards, remote monitoring and control functions, load analytics, energy flow visualization, battery health tracking, and automated charging management. These features empower facility managers to adopt data-driven strategies and optimize the availability of charging stations. Additionally, utilizing an Energy Management System (EMS) or intelligent control software allows the hybrid inverter to monitor solar generation, battery status, and EV charging demand in real time. This results in efficient resource dispatch, enhanced utilization, and improved predictive battery charging capabilities.
Factors to Consider Before Installing a Solar Hybrid Inverter
Installing a Solar Hybrid Inverter is a strategic investment that can transform how your facility manages energy, controls costs, and ensures uninterrupted operations. But to unlock its full potential, businesses must carefully evaluate a few critical factors before commissioning the system.
1. Evaluate Your Load Profile
To select the appropriate capacity for a Solar Hybrid Inverter, it is crucial to evaluate both continuous load (kW) and peak/surge load (kVA), particularly in scenarios involving heavy machinery, motors, or compressors. Additionally, consideration of future load growth is essential, as additional or more demanding processes could necessitate a larger inverter. Each industrial setting possesses distinct energy demands; thus, a comprehensive understanding of daytime load, peak load, and critical backup requirements is necessary to ensure the inverter selected can maintain smooth operations without risk of overloads or power instability.
2. Battery Selection & Compatibility
When selecting a solar hybrid inverter, it is crucial to ensure compatibility with the battery chemistry you intend to utilize, such as lithium-ion, LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate), or lead-acid. It is essential to match the battery’s capacity (measured in kWh) with your load requirements and desired backup duration during outages. Evaluate the inverter’s support for Depth of Discharge (DoD), charge/discharge rates, and integration with a Battery Management System (BMS). The battery bank is a vital component of a hybrid system, so it is important to consider factors like backup hours, depth of discharge, round-trip efficiency, and the long-term lifecycle of the batteries in order to maximize return on investment (ROI).
3. MPPT Range & Solar Panel Configuration
The text discusses the importance of Multiple Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) channels in solar energy systems, particularly for larger or more complex photovoltaic (PV) arrays that may have different roof orientations. It emphasizes that a powerful solar hybrid inverter should include multiple MPPTs to enhance compatibility with the solar array design. Additionally, having a wider MPPT voltage range is highlighted as a factor that leads to improved system performance, increased energy generation, and greater design flexibility.
4. Grid Conditions & Power Quality Requirements
To determine the appropriate inverter for your energy system, consider whether you prefer grid-tied, off-grid, or hybrid/grid-forming operation. Hybrid inverters can vary; some function independently (island mode), while others require a connection to the grid. Ensure that the inverter supports essential transfer modes, including zero-interruption switch over, black start, or islanding, as needed. Also, verify compatibility with local grid standards, specifically voltage and frequency. In industrial environments, where voltage fluctuations and instability are common, it is crucial to select an inverter that can manage wide grid variations, supports islanding, offers a seamless switchover, and maintains stable output to protect sensitive machines and optimize productivity.
5. Space, Ventilation & Environmental Factors
Hybrid inverters require careful consideration regarding heat generation and ventilation for optimal performance and lifespan. It is essential to install the unit in a dust-free, moisture-controlled environment with good airflow. When installing outdoors, choose inverters with high ingress protection (IP) ratings suitable for the environmental conditions. Factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and dust levels need to be evaluated to ensure the inverter operates effectively. Additionally, adequate space must be maintained around the inverter to facilitate ventilation and heat dissipation.
6. Wiring & Protection
To ensure an efficient and safe installation of Solar Hybrid Inverters, it is crucial to use appropriately sized and high-quality cabling to prevent voltage drops, as poor wiring is a frequent mistake. Install DC disconnects between solar panels and the inverter, along with implementing essential surge protection, earthing, and necessary protection devices. Compliance with local electrical codes, safety standards, and utility regulations is mandatory. Furthermore, the installation must encompass proper DC isolators, surge protection measures, earthing systems, breakers, and safe wiring practices. Adhering to these guidelines is vital for preventing outages and inefficiencies while enhancing safety in the installation process.
7. Smart Monitoring & Remote Management
Choose hybrid inverters with remote monitoring capabilities such as Wi-Fi, Modbus, CAN, or cloud dashboards to effectively track performance, battery health, and energy flows. It is essential that the system supports various energy management strategies, including peak-shaving, self-consumption, and backup, tailored to meet specific operational objectives. Industrial users will find significant advantages in utilizing advanced monitoring platforms. Therefore, selecting a Solar Hybrid Inverter with features like real-time dashboards, remote diagnostics, performance analytics, and integration with energy management systems is crucial for achieving comprehensive visibility and enhanced control over energy usage.
8. Reliability, Warranty & Service Support
It is essential to verify the manufacturer’s warranty, which typically ranges over 10 years, along with the availability of local service and spare parts when considering a hybrid system as a long-term investment. Selecting manufacturers that provide robust warranties, dependable after-sales support, and demonstrated field performance is crucial. Furthermore, service availability and access to spare parts are equally important as the specifications presented. When assessing reliability, one should review metrics, identify protection features such as overcurrent, short-circuit, and anti-islanding capabilities, and evaluate the inverter’s expected lifetime.

Challenges & Considerations
While a Solar Hybrid Inverter offers exceptional advantages—energy savings, backup power, and smart energy management—there are also practical challenges that industries must evaluate to ensure smooth integration and long-term performance. Understanding these considerations helps businesses plan better and maximize ROI.
1. Higher Initial Investment
Hybrid inverters have a higher cost compared to basic grid-tied inverters, primarily due to the requirements for additional electronics, battery integration, and control systems. This necessity for a compatible battery bank and potentially extra components contributes to increased upfront capital expenditures (CAPEX). Consequently, a Solar Hybrid Inverter system is generally more expensive than traditional grid-tied setups, as it incorporates battery storage and advanced control mechanisms. Industries must consider factors such as payback periods, available subsidies, and long-term operational savings in order to make well-informed financial decisions regarding investment in these systems.
2. Battery Costs & Maintenance
The performance and reliability of a hybrid system are heavily reliant on the battery, with its life span, including cycles, depth-of-discharge, and capacity degradation, playing a critical role. Batteries may need to be replaced after a few years, leading to increased long-term costs. The choice of battery significantly impacts both the overall system cost and its performance. Lithium-ion batteries, while offering superior performance, come at a higher price, whereas lead-acid batteries are more economical but necessitate greater maintenance. Incorrect battery selection or sizing can lead to decreased efficiency within the Solar Hybrid Inverter system.
3. Complexity in System Design
Installing a hybrid solar system, which includes an inverter, battery, solar panels, and a connection to the grid or a diesel generator (DG), is a sophisticated process compared to a standard solar-only setup. This installation necessitates meticulous planning, the involvement of qualified engineers or technicians, appropriate wiring, safety equipment, and occasionally structural adjustments. Hybrid systems incorporate solar power, a grid connection, and battery storage, all coordinated by a Solar Hybrid Inverter. Due to this intricate design, significant expertise is required to ensure efficient operation and to prevent potential issues such as overloading, diminished efficiency, or component incompatibility.
4. Dependence on Battery Health
During protracted cloudy conditions or low solar generation, reliance on the grid or backup diesel generators (DG) becomes necessary, especially when battery capacity is inadequate or when batteries are compromised due to degradation. An unstable grid, coupled with improper battery management, can lead to reduced reliability. The performance of a Solar Hybrid Inverter is fundamentally linked to the quality of the battery being used. Factors such as deep discharges, overheating, improper charging practices, or ineffective Battery Management Systems (BMS) can lead to shorter backup durations, decreased efficiency, and an increase in long-term operational costs.
5. Technical Skill Requirement
Proper battery management systems (BMS) necessitate regular technical checks and correct installation to ensure optimal performance and safety. Unskilled maintenance can result in diminished battery life and safety hazards. Similarly, a Solar Hybrid Inverter requires skilled technicians for installation, configuration, and maintenance. Inadequate commissioning can result in inefficiencies, energy losses, and premature failures in the system, highlighting the importance of selecting a qualified EPC partner.
6. Long-Term Service Support
The design of a solar power system is critical for achieving its intended benefits, such as backup support and cost savings. If elements like the battery are undersized, ventilation is inadequate, or maintenance is poor, the expected return on investment (ROI) can be negatively impacted due to increased lifetime costs from battery replacements and repairs. The Solar Hybrid Inverter plays a pivotal role within this system; however, issues like limited service availability, weak warranty policies, or a lack of spare parts can result in prolonged downtime and diminished operational reliability.
Latest Trends in Solar Hybrid Inverters
1. Advanced Power Electronics — More Efficiency, Higher Power Density
Modern hybrid inverters are adopting advanced semiconductor materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN), which facilitate faster switching, higher power densities, and reduced energy losses. This leads to improved overall conversion efficiency, allowing for more compact inverters that produce less heat and provide increased reliability. Such enhancements are particularly beneficial for industrial-scale photovoltaic (PV) and battery systems, where every fraction of efficiency plays a crucial role.
2. Hybrid + Storage + Smart Inverter → The New Baseline
Solar hybrid inverters, which integrate solar photovoltaic (PV) conversion, battery storage management, and grid interaction, are increasingly becoming a standard requirement in new commercial and industrial installations rather than remaining a niche solution. This trend is reflected in recent EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) tenders that increasingly demand “storage-ready” systems as a baseline, indicating a notable shift in industry norms. The movement towards hybrid inverters corresponds with a rising focus on energy autonomy, resilience, and the optimization of self-consumption, shifting the industry’s attention beyond mere solar generation.
3. Integration of Smart Energy Management, IoT, AI & Remote Monitoring
Hybrid inverters are advancing into sophisticated energy management hubs through the integration of IoT connectivity, cloud-based monitoring, and AI/ML-driven optimization, alongside predictive maintenance functionalities. The implementation of real-time dashboards, remote diagnostics, energy-flow analytics, and predictive alerts is enhancing the operational oversight for facility managers, offering them improved visibility and control over energy systems. For industrial clients, these advancements contribute to decreased downtime risk, enhanced maintenance planning, and more intelligent load and storage scheduling, thus optimizing energy management and operational efficiency.
4. Modular, Scalable & Flexible System Architecture
Solar hybrid inverter systems are increasingly utilizing modular designs to accommodate fluctuating and expanding energy demands. This approach facilitates easy scalability by allowing the addition of more panels, batteries, or inverter units as needed. Such flexibility is particularly advantageous for manufacturing units or industrial parks contemplating phased expansions, as it eliminates the necessity to over-size the system initially. Modular systems reduce entry-cost barriers and support future upgrades, making them a viable option for industries looking to grow efficiently over time.
5. Energy Storage & Battery Technology Integration — Better Batteries + Wider Compatibility
Hybrid inverters are evolving to integrate with advanced battery technologies such as lithium-ion and lithium iron phosphate (LFP), moving beyond traditional lead-acid batteries. The decreasing costs and improving energy densities of batteries enhance the viability of solar plus storage systems, leading to advantages such as extended backup power, increased self-consumption, and peak-shaving capabilities. This trend empowers providers to present clients with more comprehensive solutions, transitioning from standard grid-tied solar installations to complete solar systems with integrated storage and backup functionality.
6. Grid-Forming & Micro-Grid–Ready Capabilities
Hybrid inverters are adapting to address rising grid instability and the demand for energy resilience by offering functionalities such as grid-forming, island-mode, and microgrid-ready operations. These features prove especially beneficial for industrial sites, remote locations, and facilities requiring consistent uptime during grid outages. With the increasing prevalence of distributed energy resources (DERs), grid-forming hybrids play a crucial role in stabilizing local voltage and frequency, thereby enhancing overall grid resilience.
7. Market Maturity, Cost Reduction & Wider Adoption
As competition increases and manufacturers enhance production capabilities, the costs associated with solar hybrid inverters and balance-of-system (BOS) components are declining. This price reduction makes solar + storage systems more economically appealing to buyers. The trend prompts more industrial and commercial purchasers to explore hybrid setups as alternatives to conventional solar-only systems. Additionally, it creates opportunities in previously underserved market segments such as smaller factories, small and medium enterprises (SMEs), and multi-site operations, where hybrid systems become a feasible option.
Why Solar Hybrid Inverters Are the Future of Industrial Solar
Solar hybrid inverters are rapidly becoming the future of industrial solar because they offer a level of reliability, intelligence, and cost-efficiency that traditional systems simply cannot match. As industries face rising energy costs, stricter sustainability mandates, and growing production demands, the Solar Hybrid Inverter emerges as a powerful solution that integrates solar generation, battery storage, and grid support into one smart platform.
This technology ensures uninterrupted power during grid failures, reduces dependency on diesel generators, and significantly lowers operational expenses by intelligently switching between solar, battery, and grid supply based on real-time conditions. For manufacturing units that rely on stable voltage for heavy machinery, hybrid inverters deliver superior power quality with reduced harmonics and consistent voltage output, protecting equipment and extending its lifespan. They also offer advanced monitoring through IoT-enabled dashboards, giving facility managers complete visibility and control over energy production and consumption.
What makes hybrid inverters truly future-ready is their scalability — businesses can easily add more panels, expand battery capacity, integrate EV charging, or transition into microgrid operations without redesigning the entire system. By improving energy autonomy, enhancing sustainability performance, and supporting long-term expansion, the Solar Hybrid Inverter has become the cornerstone of modern industrial energy strategy and a key driver of smarter, cleaner, and more resilient industrial operations.
Why Choose an Experienced EPC Partner for Hybrid Solutions
Choosing an experienced EPC partner for hybrid solar solutions can make all the difference between a system that merely works and one that consistently delivers high performance, long-term savings, and uninterrupted energy reliability. A seasoned EPC team understands the complexities of integrating solar, battery storage, and hybrid inverter technologies into existing industrial infrastructures. They bring deep technical expertise, proven engineering practices, and the ability to anticipate and mitigate challenges—whether related to load management, grid synchronization, safety compliance, or future scalability.
Their industry knowledge ensures precise system sizing, optimized power flow, and seamless commissioning, allowing manufacturers to maximize uptime, reduce energy costs, and enhance operational resilience. With an expert EPC partner, industries gain not just a project executor but a long-term energy ally who ensures quality installation, proactive maintenance, and tailored solutions designed for sustained growth in an increasingly energy-demanding world.
Conclusion
As industries move toward smarter, more resilient energy systems, hybrid solar solutions are emerging as a powerful catalyst for long-term efficiency and operational stability. But the true impact of this technology depends on the expertise behind it. Partnering with an experienced EPC provider ensures precision engineering, seamless installation, reliable performance, and future-ready scalability—key ingredients for reducing energy costs and unlocking uninterrupted productivity. In a rapidly changing energy landscape, choosing the right EPC partner isn’t just a decision… it’s a strategy for staying competitive.
Ready to future-proof your facility with a high-performance hybrid solar solution?
Connect with our expert team today and discover how we can turn your solar goals into real, measurable results. Let’s build an energy system that powers your growth for years to come.