As the world shifts towards sustainable energy solutions, solar power stands at the forefront of this transition. To make solar energy accessible and affordable, many countries, including India, the UK, the USA, and Australia, have introduced various solar panel scheme government initiatives. These schemes aim to promote clean energy adoption, reduce carbon footprints, and support citizens financially through subsidies, rebates, and tax incentives.
Table of Contents
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the solar panel scheme government initiatives—how they work, their benefits, who can apply, and how they can transform your energy costs and lifestyle.
What Is a Solar Panel Scheme Government Initiative?
A solar panel scheme government initiative is a program launched by the Indian government to promote the use of solar energy among households, businesses, farmers, and industries. These initiatives aim to make solar power more affordable, accessible, and widespread by offering financial incentives such as subsidies, low-interest loans, and simplified installation processes. The primary goals of these programs are to reduce dependence on fossil fuels, lower electricity bills for citizens, promote clean and renewable energy, and help India meet its ambitious renewable energy targets.
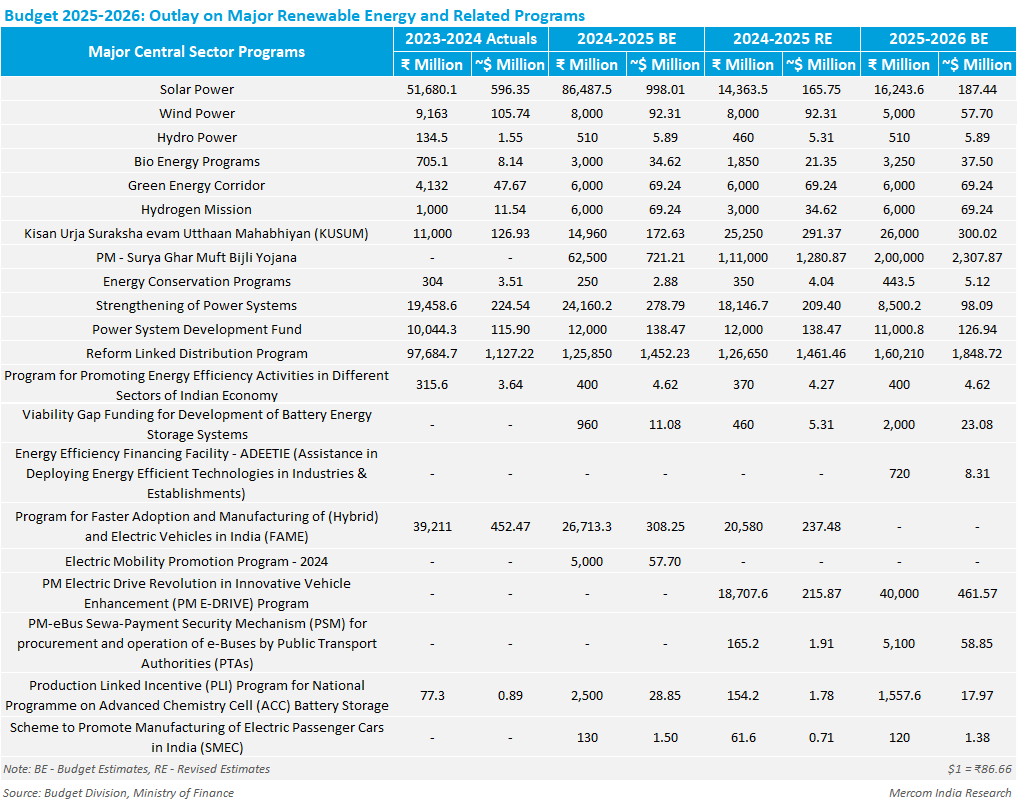
In 2025, key government solar panel initiatives include the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, which provides free electricity to 1 crore households through rooftop solar installations, and the PM-KUSUM Scheme, which provides energy security to farmers by installing solar pumps and grid-connected solar power plants. State-specific initiatives like Gujarat’s Suryashakti Kisan Yojana empower farmers to install solar panels on their farms.
Benefits of these schemes include financial savings, environmental impact, energy security, and economic growth. Financial savings include reduced electricity bills and potential income from surplus energy sold back to the grid. Environmental impact includes decreased carbon footprint and promotion of clean energy, energy security enhances energy independence for households and farmers, and job creation in the renewable energy sector stimulates local economies.
Interested individuals can apply for these schemes through official portals, providing necessary documents such as identification proof, electricity bill, KYC documents, address proof, and proof of property ownership.
Why Governments Are Investing in Solar Panel Schemes
Several critical reasons drive government investment in solar panel scheme government programs:
Reducing Carbon Emissions
One of the primary motivations is to alleviate the financial burden of electricity bills on households. For instance, India’s PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana aims to provide free electricity to 1 crore households by facilitating rooftop solar installations. Eligible households can receive subsidies up to ₹78,000, depending on the system’s capacity. This initiative is projected to help poor and middle-class households save up to ₹15,000 to ₹18,000 crores annually by getting free solar electricity and selling surplus power to electricity distribution companies.
Achieving Climate and Renewable Energy Goals
Governments are committed to reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. In India, the National Solar Mission aims to establish the country as a global leader in solar energy by creating policy conditions for its diffusion across the country. The mission’s objective is to promote ecological sustainable growth while addressing India’s energy security challenges.
Enhancing Energy Security and Independence
By promoting decentralized energy production through rooftop solar installations, these schemes enhance energy security and reduce transmission losses. Generating your own solar power can give you the freedom to keep the lights on if there’s a disruption in power.
Empowering Rural and Underserved Communities
Solar panel schemes are instrumental in bringing electricity to remote and underserved areas. For example, Gujarat’s Suryashakti Kisan Yojana empowers farmers to install solar panels on their farms, offering a 60% subsidy and a 30% loan at 4.5–6% interest, with the remaining 10% borne by the farmers.
Demonstrating Global Leadership in Renewable Energy
By investing in solar panel schemes, governments position themselves as leaders in the global transition to renewable energy. India’s commitment to expanding its solar capacity through initiatives like the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana and the National Solar Mission underscores its role in driving global renewable energy adoption.
Reducing Government Expenditure on Energy Subsidies
By enabling households to generate their own electricity, governments can reduce the financial burden of energy subsidies. The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana is projected to help the government save around ₹75,000 crore per year in electricity costs.
Types of Solar Panel Scheme Government Initiatives
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana
Launched in February 2024, this flagship scheme aims to provide free electricity to 1 crore households by facilitating rooftop solar installations. Eligible households can receive subsidies up to ₹78,000, depending on the system’s capacity. Additionally, beneficiaries can avail collateral-free loans up to ₹2 lakh at a subsidized interest rate of 6.75% through 12 public sector banks, making solar installations more accessible.
PM-KUSUM Scheme (Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan)
This scheme focuses on providing energy security to farmers by installing solar pumps and grid-connected solar power plants. Under this scheme, farmers receive a subsidy ranging from 30% to 90% for installing solar pumps, reducing their dependence on diesel and lowering irrigation costs.
Grid-Connected Rooftop Solar Programme
Under the aegis of the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), this program targets the installation of 40,000 MW by 2026, with a focus on residential sectors. It offers Central Financial Assistance (CFA), covering 40% of costs for systems up to 3 kW and 20% for systems between 3 kW and 10 kW, plus incentives for communal facilities in housing societies.
Development of Solar Parks and Ultra Mega Solar Power Projects
This initiative aims to set up at least 25 solar parks and ultra mega solar power projects, targeting 20,000 MW of solar power installed capacity within a span of 5 years starting from 2014-15. The capacity of the scheme was enhanced from 20,000 MW to 40,000 MW on 21-03-2017.
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for High-Efficiency Solar PV Modules
This scheme provides financial incentives to selected solar PV module manufacturers for five years post commissioning, on manufacture and sale of high-efficiency solar PV modules.
Off-Grid Solar Schemes
These schemes aim to provide solar energy solutions to remote and underserved areas. For instance, the New Solar Power Scheme targets Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG) habitations/villages under the PM JANMAN initiative.
Central Public Sector Undertaking (CPSU) Scheme Phase-II
This scheme aims to set up 12 gigawatts of solar projects by state-run entities, using domestically manufactured solar PV cells and modules, with financial support from the Indian government. The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) has … , moving the commissioning deadline of certain solar power projects to December 2025.
National Solar Mission
Launched in 2010, the National Solar Mission aims to establish India as a global leader in solar energy by creating policy conditions for its diffusion across the country. The mission’s objective is to promote ecologically sustainable growth while addressing India’s energy security challenges. The government revised the target from 20 GW to 100 GW on 1 July 2015, to be achieved through 60 GW of large and medium-scale solar projects and 40 GW through rooftop solar projects.

Solar Panel Scheme Government Support in the United Kingdom
As of 2025, the UK government has implemented several initiatives to support the adoption of solar panels, aiming to reduce carbon emissions, lower energy bills, and enhance energy security. These programs cater to various sectors, including low-income households, public institutions, and private homeowners. Below is an overview of the key solar panel support schemes available in the UK:
1. Energy Company Obligation (ECO4)
The ECO4 scheme, running until March 2026, mandates large energy suppliers to provide energy efficiency measures to low-income and vulnerable households. This includes the installation of solar panels, heating systems, insulation, and double glazing. Eligibility is based on receiving certain income-related benefits. In some cases, the grant has covered the cost of multiple energy upgrades costing over £80,000.
2. Warm Homes: Local Grant (WH:LG)
Introduced in April 2025 and set to run until March 2028, the WH:LG provides 100% funding for energy performance upgrades, including solar panel installations, to low-income households in England with Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) ratings between D and G. The grant is administered by local authorities, and there is no direct application process for homeowners.
3. Great British Energy (GB Energy) Initiatives
GB Energy, a state-owned energy company, has allocated £200 million to install rooftop solar panels on approximately 200 schools and 200 NHS sites across England. This initiative aims to reduce energy bills for public institutions and reinvest savings into frontline services. The first installations are expected by the end of summer 2025.
4. 0% VAT on Solar Panel Installations
To encourage renewable energy adoption, the UK government implemented a 0% VAT rate on the installation of solar panels for residential properties in 2022. This reduction lowers the upfront cost of solar installation, making solar power more accessible to homeowners.
5. Smart Export Guarantee (SEG)
The SEG scheme allows households generating electricity through solar panels to sell excess energy back to the grid. Energy suppliers with over 150,000 customers are required to offer tariffs to small-scale low-carbon generators for each unit of electricity exported. This provides an opportunity for homeowners to earn money from their solar installations.
6. Contracts for Difference (CfD)
While primarily targeting large-scale renewable energy projects, the CfD scheme offers long-term price stability to electricity generators, including solar farms. By guaranteeing a fixed “strike price” for electricity, the scheme encourages investment in renewable energy infrastructure.
Government Solar Schemes in the United States
The USA has robust solar panel scheme government support at both federal and state levels.
1. Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a 30% federal tax credit for homeowners and businesses installing solar photovoltaic (PV) systems on their primary or secondary residences. This credit applies between 2022 and 2032, with a phasedown to 26% in 2033 and 22% in 2034. The credit is popular and impactful for solar energy in the US, allowing homeowners and businesses to deduct 30% of the total cost of solar systems from their federal taxes. The credit is available to both homeowners and businesses who install solar panels on their property.
2. Solar for All Program
The Solar for All initiative, administered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), provides $7 billion in grants to expand solar access for low-income and disadvantaged communities. The program, administered by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), supports the deployment of solar installations in low-income households, aiming to reduce energy bills for vulnerable populations. The program allocates $7 billion in grants to fund solar energy projects, ensuring cleaner, cheaper energy for communities across the U.S. The initiative is typically aimed at low-income households or disadvantaged communities.
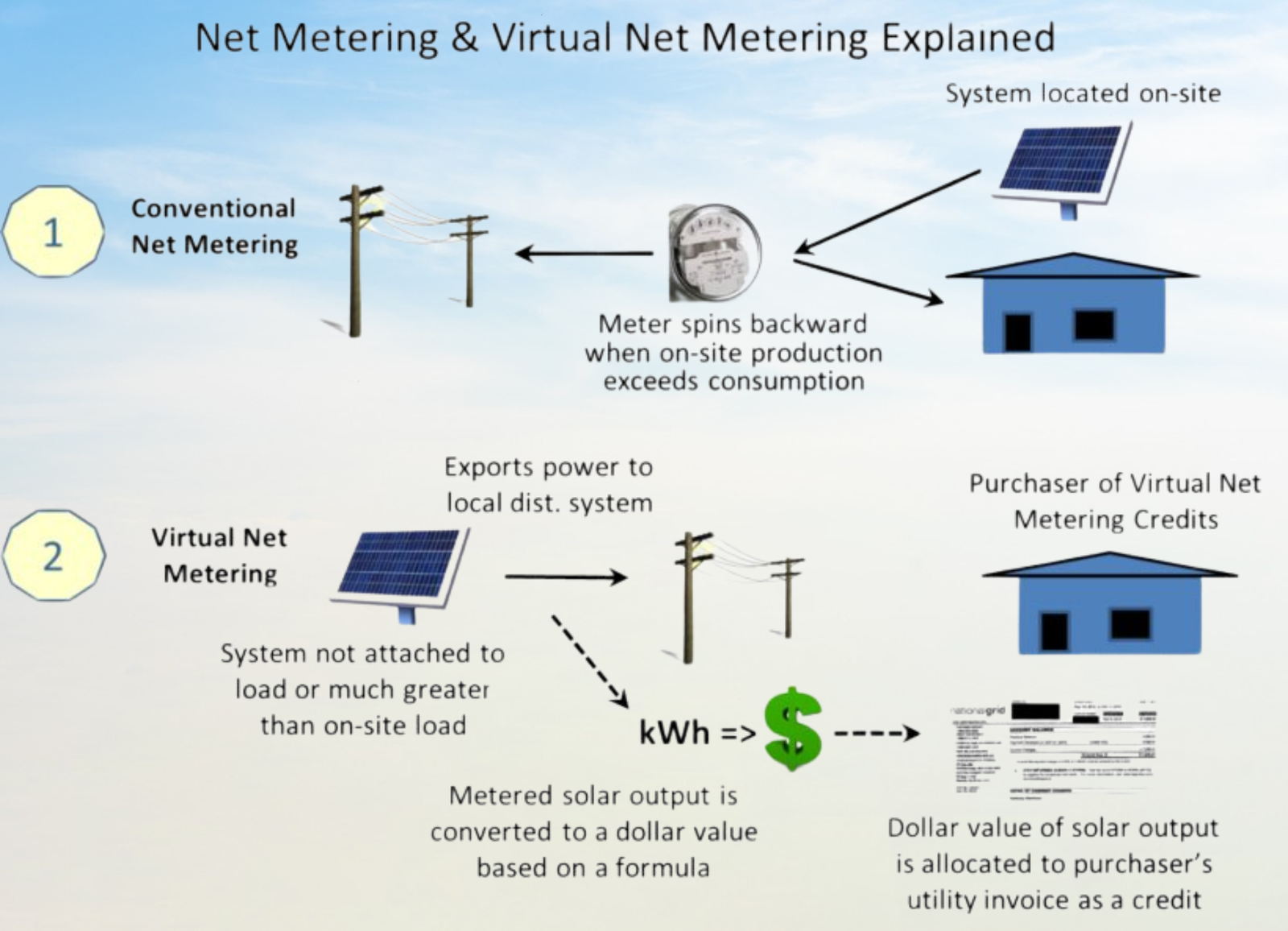
3. Net Metering Policies
Net metering is a policy that allows homeowners to sell excess electricity back to the grid, earning credits for the surplus energy generated. This can offset electricity costs during the day or during cloudy days when the solar system is not producing energy. However, net metering policies vary by state and utility provider, with some offering more favorable terms. Net metering helps homeowners offset the costs of installing solar systems by earning money or credits for excess energy generated. It’s crucial to consult local regulations to understand the specific benefits available.
Solar Panel Scheme Government Initiatives in Australia
Australia, a country abundant in sunlight, has also introduced several programs:
1. Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES)
The Small-Scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) is a program that provides financial incentives for installing solar energy systems, including solar water heaters and heat pumps. The scheme awards Small-scale Technology Certificates (STCs) based on the expected energy generation of the installed system, which can be sold or traded to reduce the upfront cost of solar panel installation. Eligible for both residential and small commercial solar installations, the STCs can be sold or assigned based on system size, location, and energy output. The scheme is ongoing but subject to changes in the number of STCs available. The duration of the scheme is subject to changes.
2. Solar Homes Program
The Solar Homes Program in Victoria provides rebates and interest-free loans to eligible households for solar system installation. The rebates help reduce installation costs, while the interest-free loans offer a repayment option over four years. Eligible households meet income criteria and own owner-occupied properties. Additionally, eligible households can apply for rebates for solar battery installations under specific conditions. The program covers existing homes, under construction homes, and rental properties. Not-for-profit community housing providers can also apply for rebates on behalf of their tenants.
3. Virtual Power Plant (VPP)
South Australia is promoting the development of a Virtual Power Plant (VPP) to connect up to 50,000 solar and battery systems statewide. This initiative, in collaboration with Tesla and Energy Locals, aims to share excess energy, contribute to grid stability, and potentially reduce energy costs. Eligible participants include homeowners, renters, and businesses that install solar and battery systems through registered VPP programs. Benefits include selling excess energy to the grid, receiving payment or credits, and potentially lowering electricity bills. The initiative is often run in partnership with private companies like Tesla and Energy Locals.
4. Tasmania: Energy Saver Loan Scheme
The Energy Saver Loan Scheme offers interest-free loans to Tasmanian residents and small businesses to install energy-efficient products, including solar systems. These loans are available to eligible households and businesses who meet certain income or other eligibility criteria. The loans typically have no establishment or account-keeping fees, making solar installation more affordable. The scheme aims to make solar adoption more accessible and affordable for Tasmanian residents and businesses.
5. Australian Capital Territory (ACT)
The Australian government’s Solar for Apartments Program aims to make solar energy more accessible to apartment dwellers by providing up to $100,000 in grants and zero-interest loans to owners’ corporations and community housing providers. The program is designed to help these entities install solar systems on apartment buildings, reducing barriers to installation and making solar energy more accessible to those who typically face barriers to installation. The program is open to not-for-profit community housing providers and apartment buildings.

Key Benefits of Solar Panel Scheme Government Programs
1. Reduced Electricity Bills
Participating in a Solar Panel Scheme Government program can significantly lower your monthly electricity expenses. For instance, India’s PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana provides up to 300 units of free electricity per month to eligible households, leading to substantial annual savings.
2. Lower Upfront Installation Costs
Solar Panel Scheme Government initiatives often offer financial incentives such as subsidies, rebates, and tax credits to reduce the initial cost of installing solar panels. In Australia, the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) allows homeowners to earn Small-scale Technology Certificates (STCs), which can be traded to offset installation costs.
3. Environmental Benefits
Adopting solar energy through Solar Panel Scheme Government programs reduces reliance on fossil fuels, decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a cleaner environment. These initiatives align with global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainable energy sources.
4. Energy Independence and Resilience
Installing solar panels, especially when combined with battery storage, enhances energy independence by reducing dependence on the grid. In areas prone to power outages, this setup ensures a reliable energy supply. Solar Panel Scheme Government programs often support such installations, promoting resilience and self-sufficiency.
5. Income Generation through Net Metering
Many Solar Panel Scheme Government initiatives include net metering policies, allowing solar panel owners to sell excess electricity back to the grid. This creates an additional income stream and maximizes the return on investment for solar installations.
6. Increased Property Value
Homes equipped with solar energy systems often see an increase in property value. Prospective buyers recognize the long-term savings and environmental benefits, making solar-equipped properties more attractive in the real estate market. Solar Panel Scheme Government incentives can make these upgrades more affordable, enhancing property appeal.
7. Enhanced Accessibility for Low-Income Households
Solar Panel Scheme Government programs aim to make solar energy accessible to all socioeconomic groups. For example, the U.S. Solar for All initiative provides grants to low- and middle-income households, facilitating solar adoption and promoting energy equity.
8. Support for Businesses and Economic Growth
Government incentives also extend to businesses, encouraging commercial adoption of solar energy. In the U.S., federal incentives can finance up to 80% of commercial solar project costs, making renewable energy a viable option for businesses and stimulating economic growth in the renewable sector.
How to Apply for a Solar Panel Scheme Government Program
Determine Your Eligibility
- To benefit from any Solar Panel Scheme Government initiative, it is essential to first determine your eligibility. These schemes typically consider several factors, including your income level, property ownership status, your home’s Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) rating, and whether you receive any qualifying government benefits. Many Solar Panel Scheme Government programs, such as ECO4, are designed specifically to assist low-income households. Homeowners or private tenants may qualify for free solar panel installation under these targeted schemes, ensuring support reaches those who need it most.
Choose the Appropriate Scheme
- UK residents can take advantage of various Solar Panel Scheme Government options in 2025, including the ECO4 Scheme, which offers free solar panels to low-income households, the Warm Homes Plan, which grants up to £30,000 for energy-efficient home upgrades, the Smart Export Guarantee, which allows surplus electricity to be sold back to the grid, zero VAT on solar panels and batteries, and Solar Together, a group-buying program that reduces prices through community participation.
Initiate the Application Process
- To apply for a Solar Panel Scheme Government initiative, follow these steps: contact your energy provider or certified provider, undergo a home assessment, and provide proof of eligibility. For the Warm Homes Plan, submit applications through the UK Government’s website or local council. For the Solar Together program, register online and provide information about your property, energy usage, and roof structure. Each program has its own guidelines, so follow them carefully.
Prepare Necessary Documentation
- To apply for a Solar Panel Scheme Government benefit, you need proof of income, property ownership or tenancy agreements, recent utility bills, and a valid EPC certificate. Accurate documentation increases your chances of approval, ensuring your home’s energy efficiency rating is demonstrated.
Undergo a Home Assessment
- Many Solar Panel Scheme Government programs require a home energy audit. This step evaluates your household’s energy usage, identifies optimal locations for panel installation, and helps determine the most effective solar energy solutions for your home. This assessment ensures the program offers you a system tailored to your specific energy-saving goals and living conditions.
Installation and Aftercare
- Once your application to a Solar Panel Scheme Government program is approved, you will schedule an installation with an accredited professional—typically one certified by the Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS). After installation, don’t forget to register for the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG), allowing you to sell excess solar energy back to the grid, providing long-term value.
Common Challenges in Availing Solar Panel Scheme Government Benefits
While the Solar Panel Scheme Government initiatives in various countries have made solar energy more accessible and affordable, several common challenges continue to hinder widespread participation. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for potential applicants looking to benefit from these schemes and for policymakers aiming to improve them.
1. Lack of Awareness and Misinformation
One of the most significant barriers to availing Solar Panel Scheme Government benefits is the general lack of awareness among eligible citizens. Many homeowners and tenants are unaware of available programs such as the ECO4 Scheme in the UK, Solar Together, or Smart Export Guarantee (SEG). In some regions, misinformation spreads quickly, leading people to miss out on genuine opportunities.
2. Complex Eligibility Criteria
Each Solar Panel Scheme Government initiative has its own set of rules and eligibility conditions. These often involve factors such as income level, homeownership status, Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) rating, and benefit receipts. For many applicants, navigating these criteria can be confusing and discouraging, especially without professional assistance.
3. Lengthy and Bureaucratic Application Processes
The process of applying for Solar Panel Scheme Government programs can be time-consuming and bureaucratic. Applicants often need to submit multiple documents, undergo home assessments, and wait for approvals from certified installers or local councils. The lack of a unified application portal adds to the complexity.
4. Insufficient Funding and Limited Capacity
Some Solar Panel Scheme Government programs have limited funding or are capped in terms of the number of participants they can accommodate each year. This means that even eligible households may be placed on waiting lists or denied support due to budget constraints.
5. High Upfront Costs (When Not Fully Covered)
Although many Solar Panel Scheme Government programs offer subsidies or free installation for qualifying households, others only provide partial support. This leaves homeowners with a significant upfront cost, which can be a deterrent—especially for low- and middle-income families.
6. Inconsistent Policy Implementation Across Regions
In many countries, implementation of Solar Panel Scheme Government benefits varies across local councils or states. This inconsistency creates confusion and inequity, as residents in some areas may have better access to solar incentives than others.

Tips to Maximize Solar Scheme Benefits
Maximizing the value of a Solar Panel Scheme Government initiative requires more than just applying for the right program—it also demands informed decisions, proper planning, and ongoing engagement. Below are practical and strategic tips to help you fully benefit from the Solar Panel Scheme Government support available in your region.
1. Research and Compare Multiple Schemes
The first step to maximizing your benefits is understanding the full range of Solar Panel Scheme Government options. In the UK, for example, these include:
- ECO4 Scheme for low-income households
- Solar Together group-buying program
- Smart Export Guarantee (SEG)
- Zero VAT Incentives on solar equipment
Each Solar Panel Scheme Government initiative has specific eligibility criteria, application methods, and benefits. Comparing them helps you choose the best option for your circumstances.
2. Check Eligibility Thoroughly
One of the most common reasons applications are rejected is incomplete or misunderstood eligibility. Carefully review the requirements of your chosen Solar Panel Scheme Government program. Key considerations include:
- Income threshold
- Property ownership status
- EPC rating of the home
- Whether you receive qualifying benefits
Meeting these prerequisites ensures smoother application processing.
3. Work with Certified Installers
Always work with Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) certified installers when engaging with any Solar Panel Scheme Government initiative. Certified professionals not only ensure compliance but also help you qualify for export schemes like SEG and avoid future legal or technical issues.
4. Get a Pre-Installation Home Assessment
Before finalizing your decision, request a home energy audit. A professional assessment helps:
- Optimize solar panel placement
- Estimate long-term savings
- Identify additional energy-saving upgrades
- Ensure your home qualifies for more than one Solar Panel Scheme Government benefit
This step boosts the efficiency and ROI of your solar installation.
5. Register for Export Incentives
Don’t stop at installation—register for programs like the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG) to sell excess power back to the grid. This adds a secondary income stream and enhances the total financial benefit of your Solar Panel Scheme Government support.
6. Claim VAT and Local Tax Exemptions
Take full advantage of tax exemptions under the Solar Panel Scheme Government initiatives. In the UK, there’s currently a 0% VAT rate on solar panels and batteries until March 2027. Also, some local councils offer reduced property taxes for energy-efficient homes.
7. Monitor Performance Regularly
Once your solar system is installed, use smart meters or monitoring apps to keep track of energy production and usage. This ensures your system operates at peak efficiency and helps you detect problems early—maintaining your eligibility for continued Solar Panel Scheme Government benefits.
8. Stay Updated on New Initiatives
The Solar Panel Scheme Government programs are frequently updated or replaced with newer policies. Subscribing to government newsletters or checking official portals ensures you’re the first to know about additional incentives or changes to existing schemes.
9. Combine with Other Green Upgrades
Maximize your benefits by combining your solar installation with other energy-efficient upgrades. Programs like the Warm Homes Plan (2025–2028) allow for bundling improvements like insulation or heat pumps, often covered under the same Solar Panel Scheme Government support.
10. Seek Expert Advice
Consult with solar energy consultants or local authorities experienced in Solar Panel Scheme Government policies. They can guide you through the maze of documents, technical evaluations, and rebate claims, helping you make the most of available resources.
The Future of Solar Panel Scheme Government Programs
The future of Solar Panel Scheme Government programs looks promising, with increasing investments and policy support to encourage the adoption of solar energy. As the global shift toward renewable energy intensifies, governments are expected to expand and improve these programs to ensure wider access to solar technology. In the coming years, there will likely be greater incentives for both residential and commercial sectors, potentially through enhanced financial support, tax rebates, and subsidies. Additionally, advancements in solar technology, such as more efficient and affordable solar panels, will make these schemes more attractive and accessible to a broader population.
Governments may also introduce more tailored solutions, considering factors like geographic location, energy needs, and environmental impact, to make solar energy even more viable for households and businesses. Furthermore, with increased public and private sector collaboration, we can expect faster installation times, smoother application processes, and more robust aftercare services. As a result, the future of Solar Panel Scheme Government programs promises to play a pivotal role in achieving national and global sustainability goals, reducing carbon footprints, and empowering individuals and communities to take control of their energy consumption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of Solar Panel Scheme Government programs is full of potential, with increasing efforts from governments worldwide to make solar energy more accessible and affordable for all. These programs will continue to evolve, providing greater incentives, smoother application processes, and enhanced technology to foster a sustainable and clean energy future. By taking advantage of these schemes, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce energy costs while contributing to a greener planet.
Now is the perfect time to explore the available Solar Panel Scheme Government options and start benefiting from renewable energy solutions. Don’t wait for the future—take action today to secure your solar panel installation and enjoy the long-term savings and environmental impact. Visit our website or contact us at Soleos Solar to learn more about how you can get involved and take advantage of government-backed solar schemes. Let’s build a sustainable future together!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can I combine multiple solar subsidies and rebates?
Answer: In many cases, yes! You can often claim both federal and state incentives.
Q2: Is the government subsidy available for solar batteries?
Answer: Some countries and regions offer separate subsidies for energy storage systems along with solar panels.
Q3: Do I have to pay taxes on solar rebates?
Answer: Generally, solar rebates are not considered taxable income, but it’s best to consult a tax expert in your region.
Q4: Are government solar schemes available for businesses too?
Answer: Absolutely. Many solar panel scheme government initiatives cater to both residential and commercial properties.
Q5: How long will government solar subsidies last?
Answer: Many programs have deadlines or decreasing benefits over time, so early adoption is recommended.